Movement
Different axis of motion evoke different emotional responses, and it is important to keep animations consistent to deliver a clear message.
Animation and kinetic interfaces have cognitive benefits for your users by reducing mental loads, and reducing change blindness. It has the ability to more effectively communicate content hierarchy and spatial relationships than static interfaces alone. Animation can reinforce your corporate brand and provide a steel thread experience across your platforms, devices, and form factors. Used responsibly, performant animation also provides accessibility benefits to those with reduced cognitive abilities.
Timing
A “grid of time” creates consistent rhythm. Animation is defined as multiples of a base grid.

Effects
Attributes are animated over time to create a vocabulary of effects.

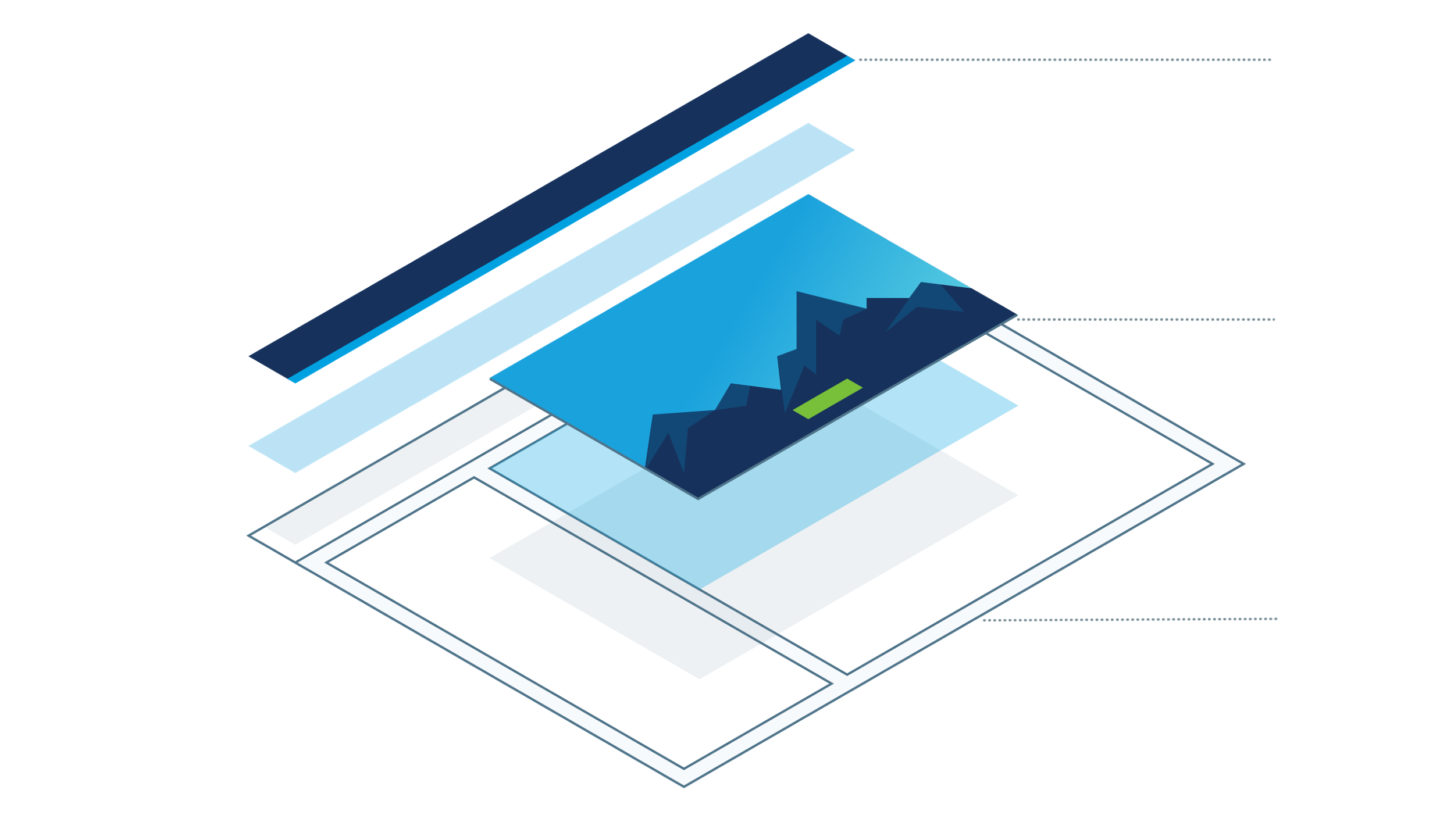
Dimension
Utilizing the Z-axis to support spatial organization aids in creating a visual hierarchy we refer to as “atmosphere”.
Timings are calculated as even multiples of 100ms which is 6 frames at 60 frames-per-second.
Short timing is greatly prefered, so that users do not feels as if they have to wait for an action to complete.
Animations should follow bezier animation curves to give objects a sense of mass and physics To get a better understanding of bezier curves, read more here and explore the example below

Effects encompase a wide variety of possible animations from transitions to micro-interactions that showcase your brand’s personality
In general animations should tend to appear less frequently (once per login) and be subtle. Again, be concious that added animations are meaningful, and not just decorative
Below is a library of animations with the code used to produce them . For more animations, head to the Component Section.
Dimension suggests a conceptual hierarchy that makes use of box shadows to indicate visual hierarchy. The actual Z-index is up to the developer to maintain the correct shadows.
Atmosphere is the virtual space in front and behind the screen. The plane of the screen has an X,Y coordinate system with 0,0 in the top left. However, the Z elevation is the imaginary normal pointed at the user, -Z descent is beyond the plane of the screen.
The elevation of an object in the atmosphere is visually rendered as box shadows. The amount of elevation is not the same as the Z-index, rather its relative elevation which aids in rendering the shadow.
Consider the example below, then head to the design tokens page for tokens to include in the CSS Box-shadow attribute

Different axis of motion evoke different emotional responses, and it is important to keep animations consistent to deliver a clear message.
Objects entering/leaving screen bounds.
Global header, progress bar, sales path
Objects indicating progress or loading state
Notifications, cards, tab content

Objects providing new information
Modals, hover states, welcome mat